The Effect of Nitrogen on Crop Growth: Why It Matters for Agriculture
Keywords: nitrogen and crop growth, nitrogen fertilizer, nitrogen in agriculture, plant nutrition, crop yield, sustainable farming
Introduction
Nitrogen is one of the most essential nutrients for plant growth, playing a vital role in agricultural productivity. As a key component of plant proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, nitrogen directly influences crop growth, yield, and quality. Farmers and agronomists alike rely on nitrogen fertilizer to enhance plant health and maximize food production. However, understanding how nitrogen works—and how to apply it effectively—is critical for both economic success and environmental sustainability.
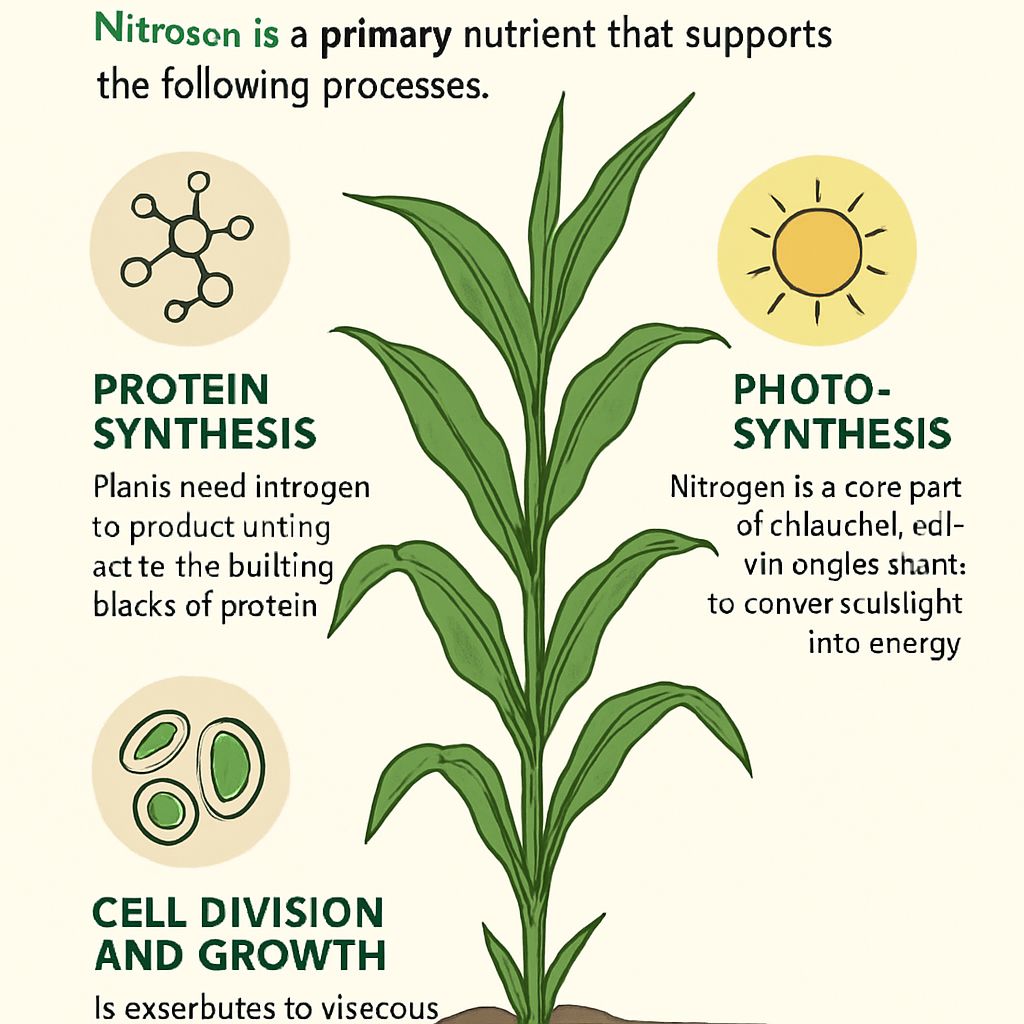
What Is Nitrogen's Role in Plant Growth?
Nitrogen is a primary nutrient that supports the following processes:
Protein Synthesis: Plants need nitrogen to produce amino acids, the building blocks of protein.
Photosynthesis: Nitrogen is a core part of chlorophyll, which enables plants to convert sunlight into energy.
Cell Division and Growth: It contributes to vigorous vegetative growth, especially in early developmental stages.
Without sufficient nitrogen, crops show signs of stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and poor yields.
Benefits of Nitrogen Fertilizer in Agriculture

Applying nitrogen fertilizer boosts crop development in several ways:
Higher Crop Yields: Adequate nitrogen levels lead to larger, healthier plants and increased grain or fruit production.
Improved Quality: In crops like wheat and corn, nitrogen enhances protein content, contributing to better nutritional value.
Faster Growth Cycles: With optimized nitrogen levels, many crops mature more quickly and efficiently.
The Downside of Overusing Nitrogen
While nitrogen is beneficial, excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers can harm the environment:
Soil Degradation: Overuse can upset nutrient balance and reduce long-term soil fertility.
Water Pollution: Nitrogen runoff contaminates rivers and lakes, leading to algal blooms and dead zones.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Nitrous oxide, a byproduct of nitrogen fertilizers, is a potent greenhouse gas.
Sustainable Nitrogen Management Practices
To ensure efficient use of nitrogen in agriculture, farmers can adopt sustainable farming practices, such as:
Precision Agriculture: Using data to apply the right amount of nitrogen at the right time.
Crop Rotation and Legumes: Rotating crops and using legumes can naturally replenish nitrogen in the soil.
Slow-Release Fertilizers: These help reduce leaching and extend the availability of nitrogen over time.
Why Our Water-Soluble Fertilizers Deliver Superior Nitrogen for Crop Health
When it comes to crop nutrition, not all nitrogen sources are created equal. That’s why it’s important to emphasize that our water-soluble fertilizers contain high-quality, plant-available nitrogen—formulated to deliver quick, effective results in the root zone.
Key Benefits of Our Nitrogen-Rich Water-Soluble Fertilizers
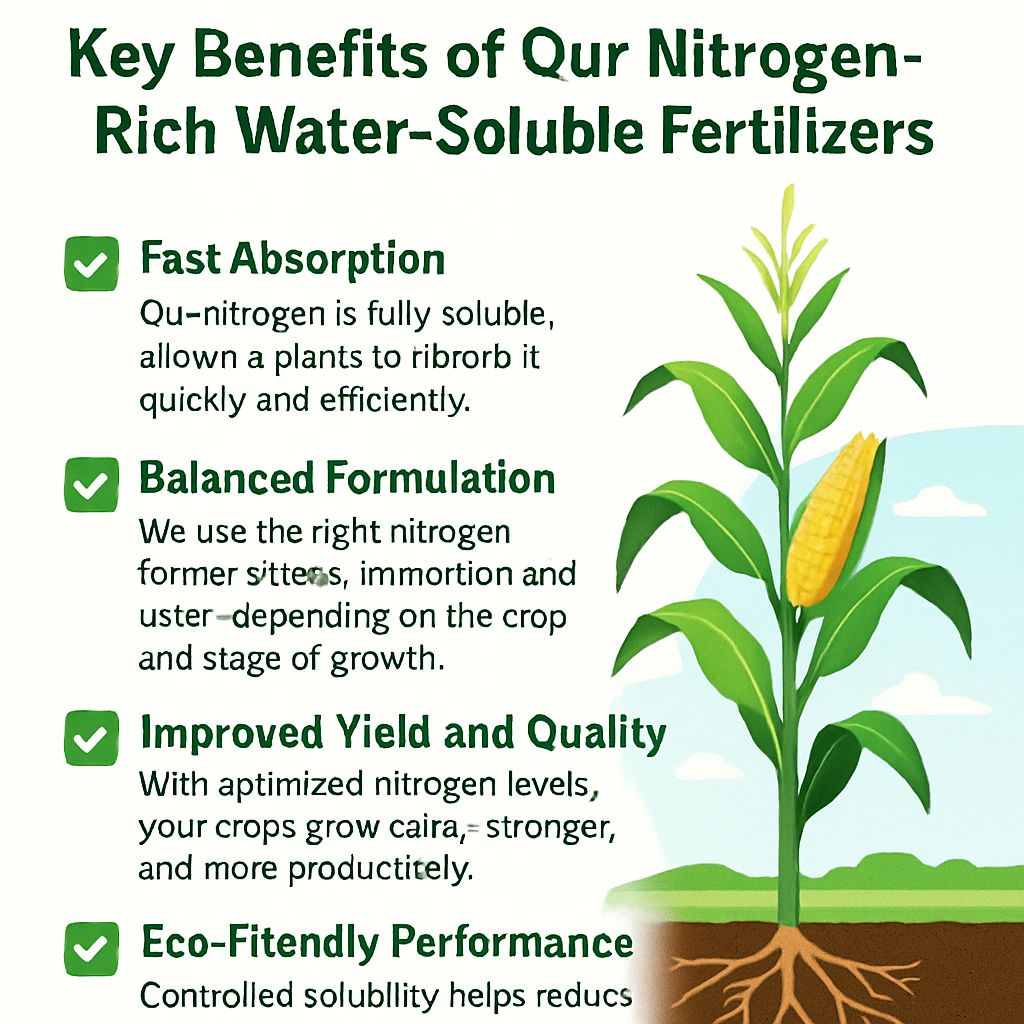
✅ Fast Absorption: Our nitrogen is fully soluble, allowing plants to absorb it quickly and efficiently.
✅ Balanced Formulation: We use the right nitrogen forms—nitrate, ammonium, and urea—depending on the crop and stage of growth.
✅ Improved Yield and Quality: With optimized nitrogen levels, your crops grow faster, stronger, and more productively.
✅ Eco-Friendly Performance: Controlled solubility helps reduce leaching and nitrogen loss, protecting both your farm and the environment.
Why Nitrogen Quality Matters
Low-grade nitrogen sources can result in uneven growth, nutrient deficiencies, and reduced yields. In contrast, our premium-grade water-soluble fertilizers ensure your crops receive consistent, reliable nutrition at every growth stage. Whether you're growing vegetables, fruits, or grains, our nitrogen formulation supports maximum uptake and minimal waste.
Conclusion
Nitrogen is a cornerstone of plant nutrition and a major factor in crop productivity. However, to maximize its benefits and protect the environment, farmers must apply nitrogen carefully and sustainably. By understanding how nitrogen works and implementing modern farming techniques, agriculture can thrive while safeguarding future generations.

 English
English Español
Español


